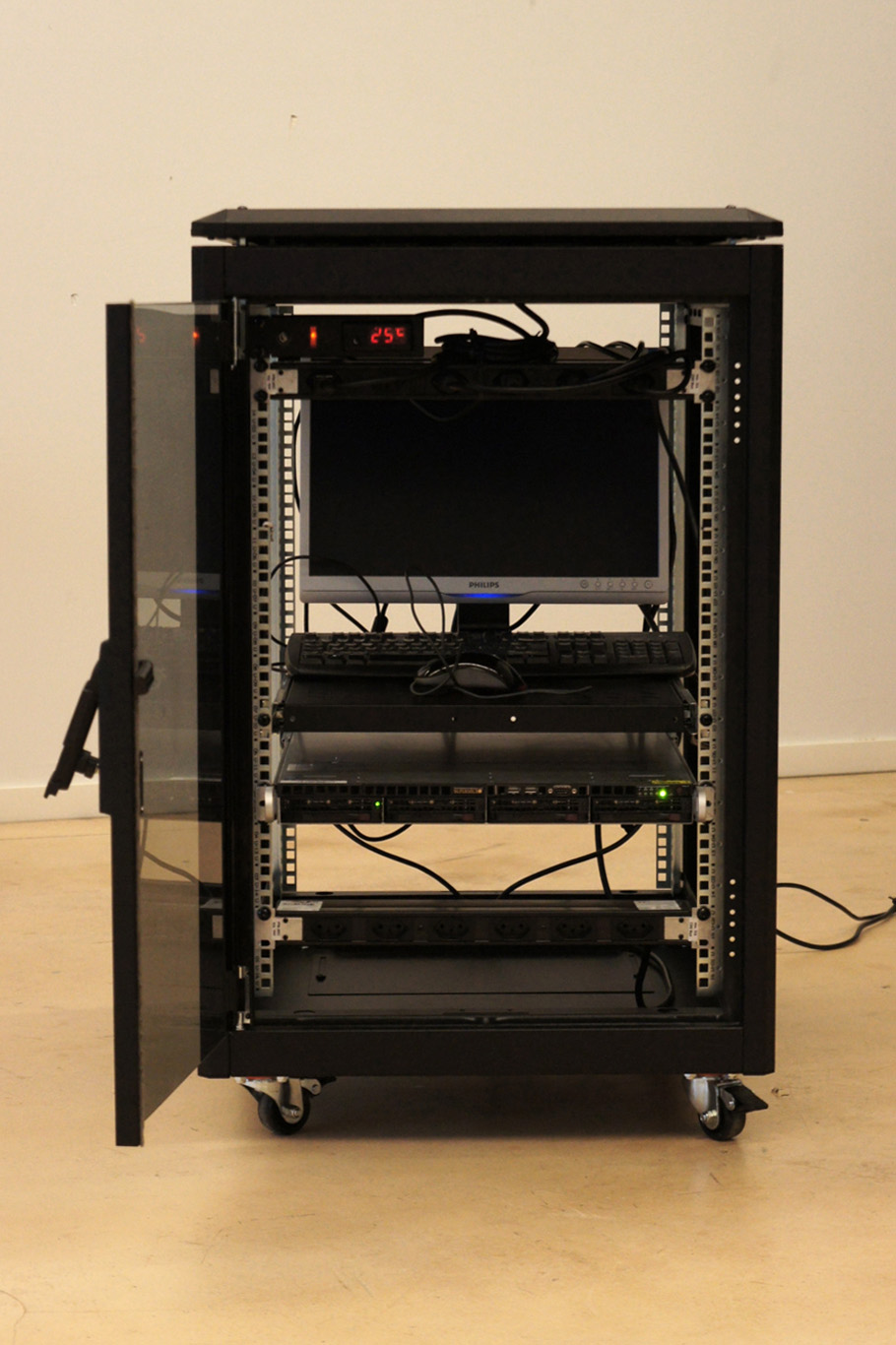
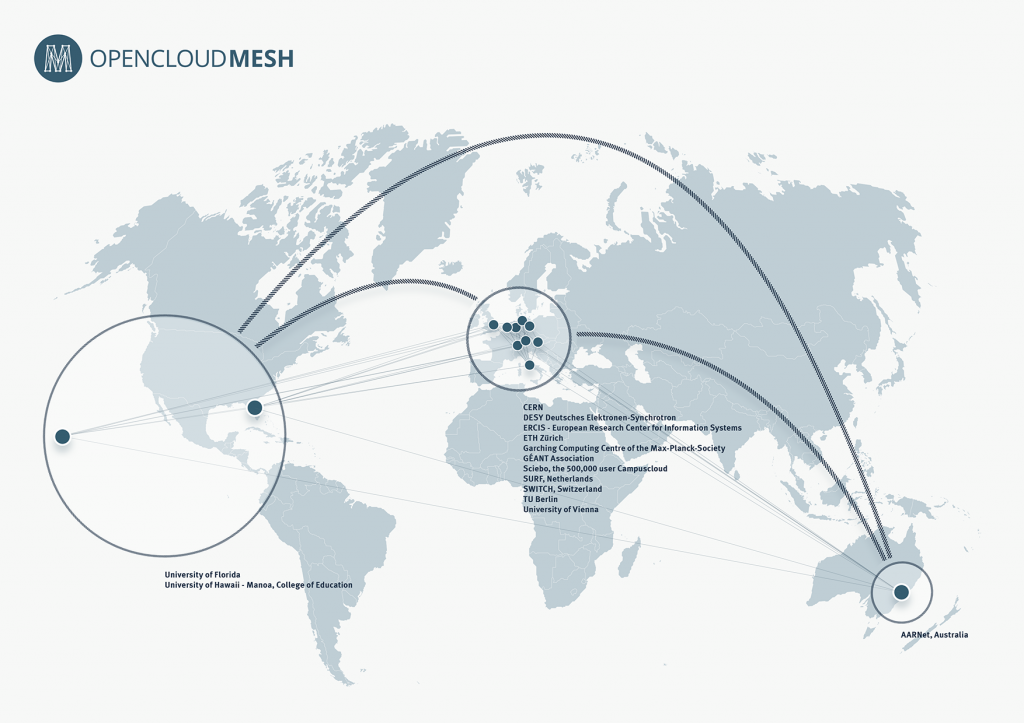
Note: When we had to pick an open source cloud computing platform at the start of our research, we dug for some time to pick the one that would better match with our planned activities. We chose ownCloud and explained our choice in a previous post, so as some identified limitations linked to it. Early this year came this announcement by ownCloud that it will initiate “Global Interconnected Private Clouds for Universities and Researchers” (with early participants such has the CERN, ETHZ, SWITCH, TU-Berlin, University of Florida, University of Vienna, etc.) So it looks like we’ve picked the right open platform! Especially also because they are announcing a mesh layer on top of different clouds to provide common access across globally interconnected organizations.
This comforts us in our initial choice and the need to bridge it with the design community, especially as this new “mesh layer” is added to ownCloud, which was something missing when we started this project (from ownCloud version 7.0, this scalability became available though). It now certainly allows what we were looking for: a network of small and personal data centers. Now the question comes back to design: if personal data centers are not big undisclosed or distant facilities anymore, how could they look like? For what type of uses? If the personal applications are not “file sharing only” oriented, what could they become? For what kind of scenarios?