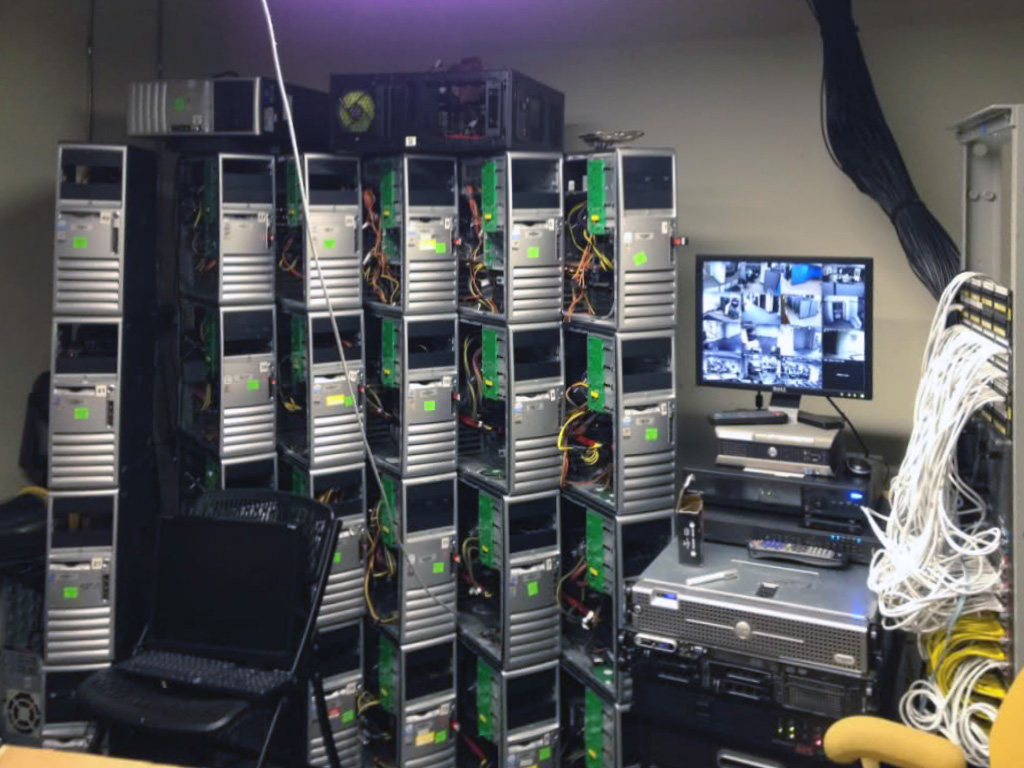
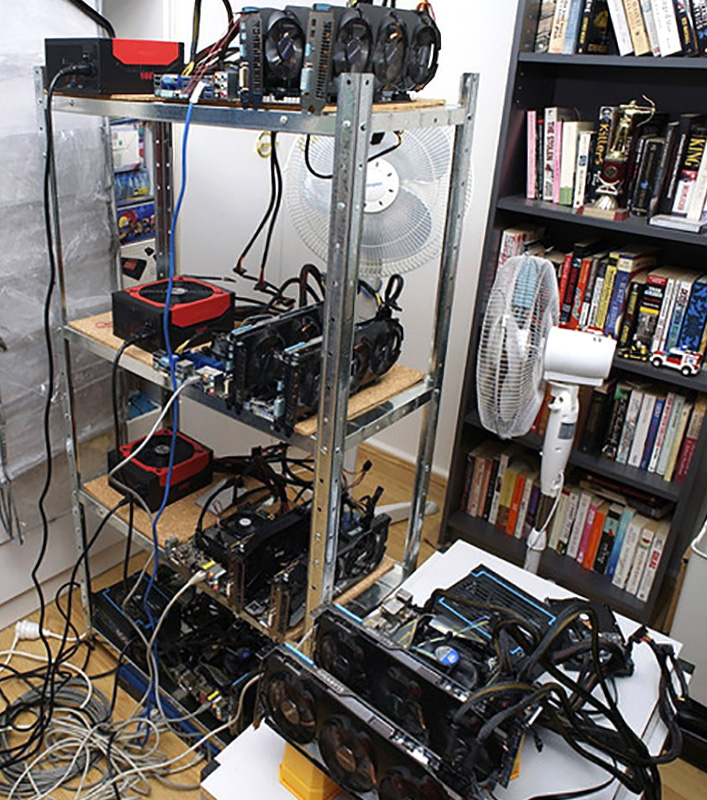
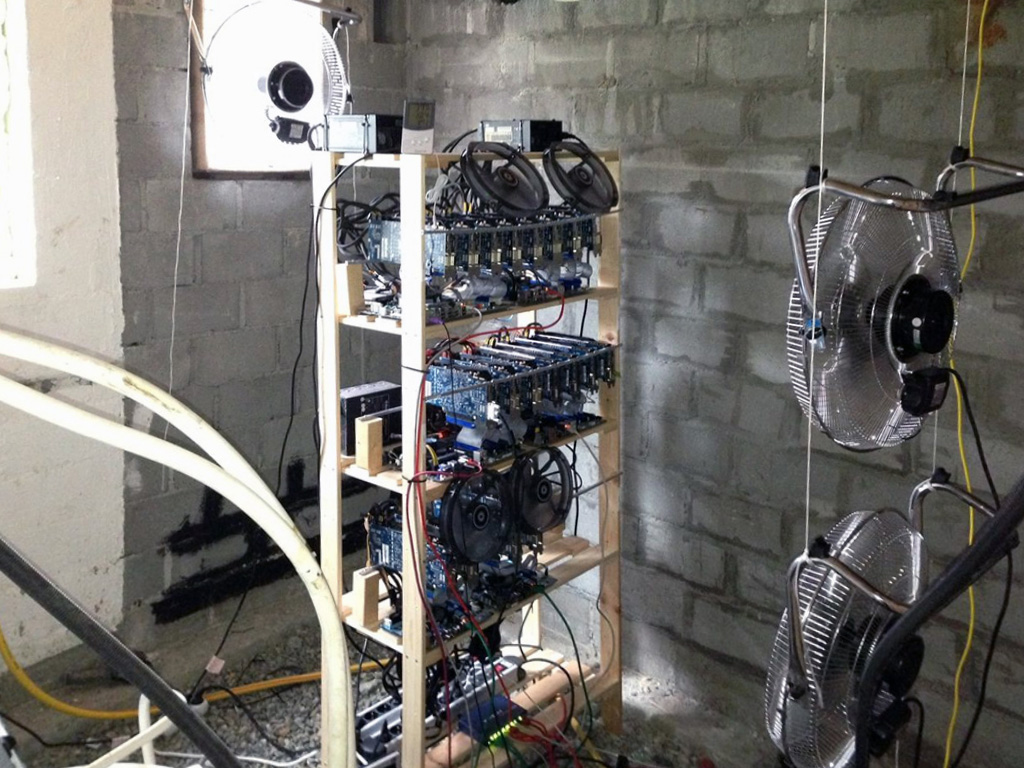
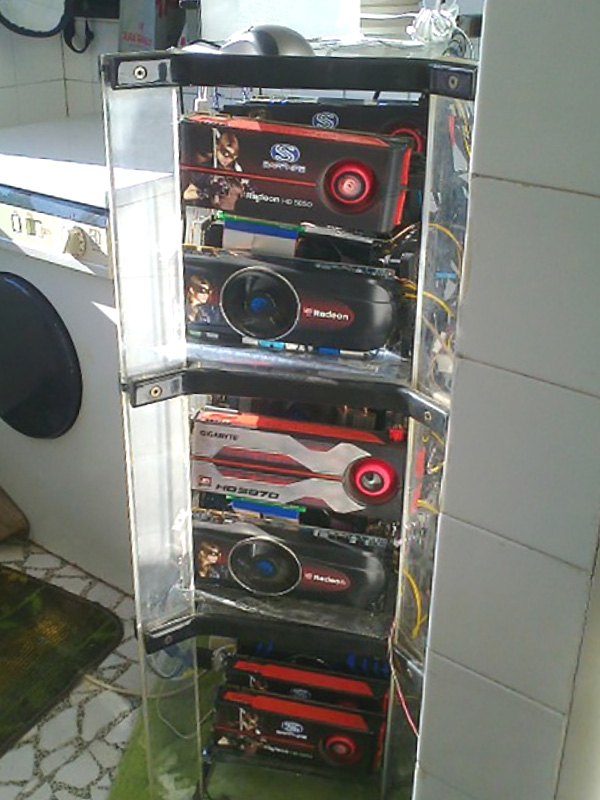
The following text was written as a description of our goals later in 2013, prior to the start of the project. The structure of the text follows the given guidelines. So to say, to get financing.
It is nonetheless a blueprint of what we intend to do and is published on the I&IC blog as a matter of documentation.
—
Inhabiting and Interfacing the Cloud(s)
An intredisciplinary design research project under the co-direction of Prof. Patrick Keller (ECAL) and Nicolas Nova (HEAD). With the support of HES-SO and the collaboration of ECAL, HEAD, EPFL (Prof. Dieter Dietz) and EPFL+ECAL Lab (Dir. Nicolas Henchoz).
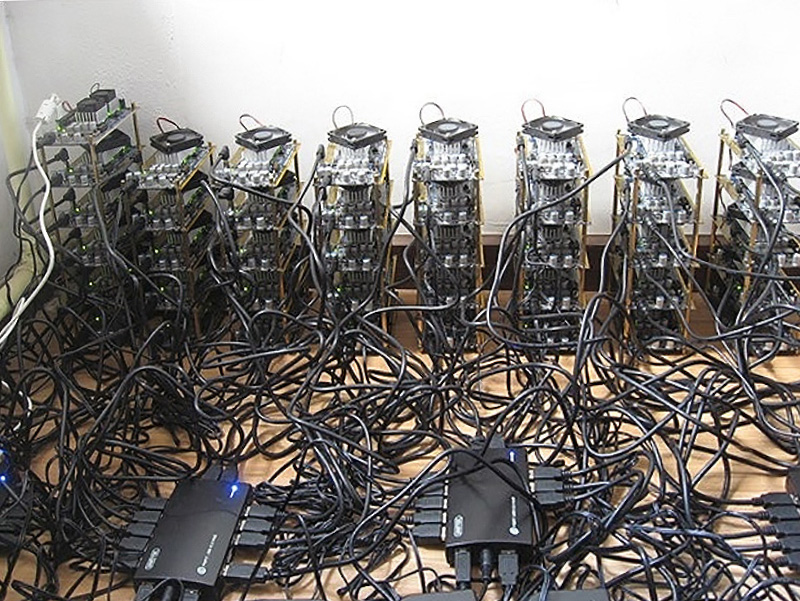
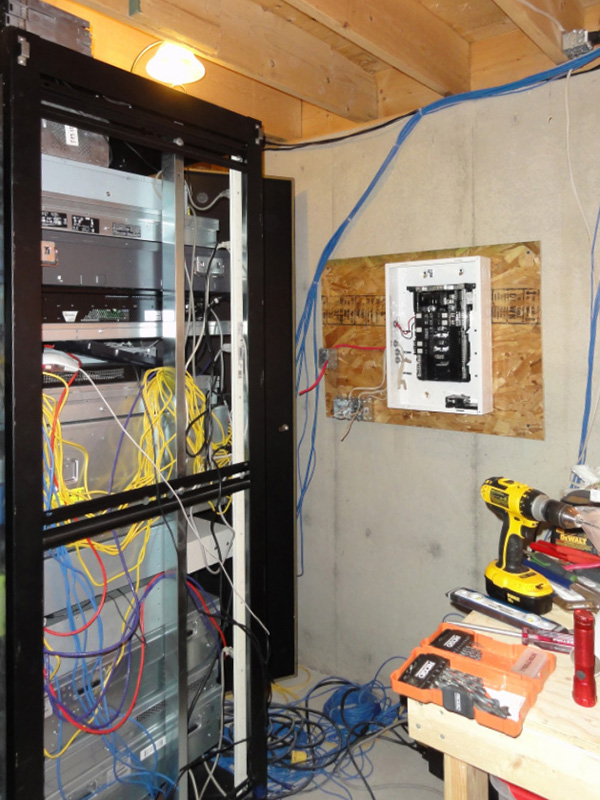
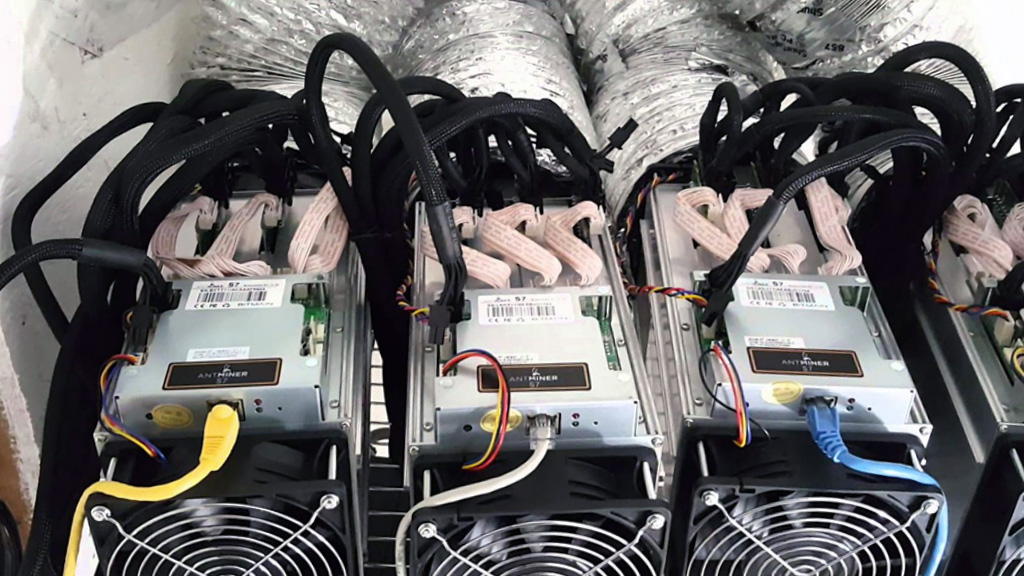
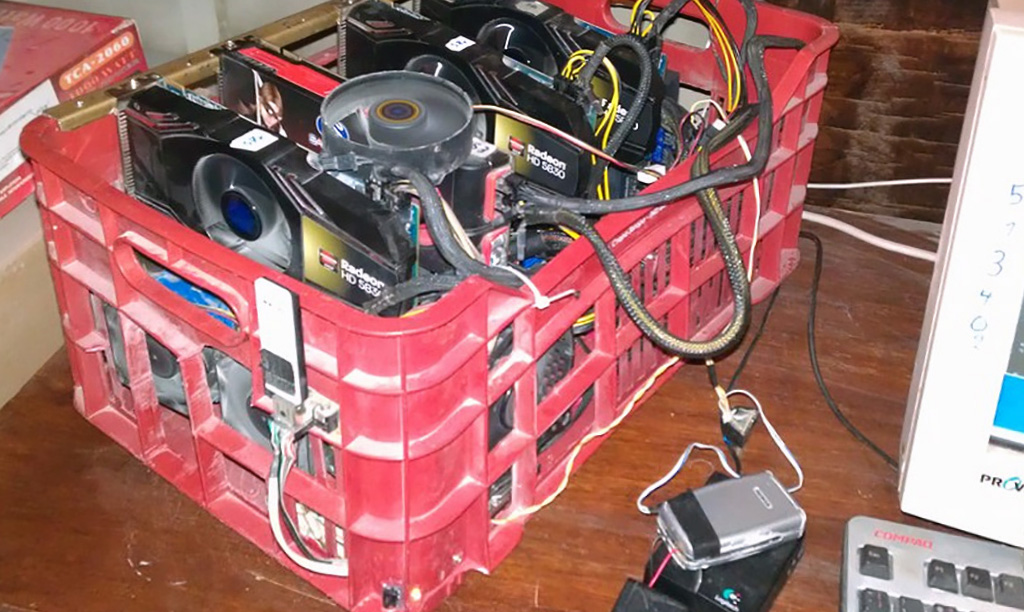
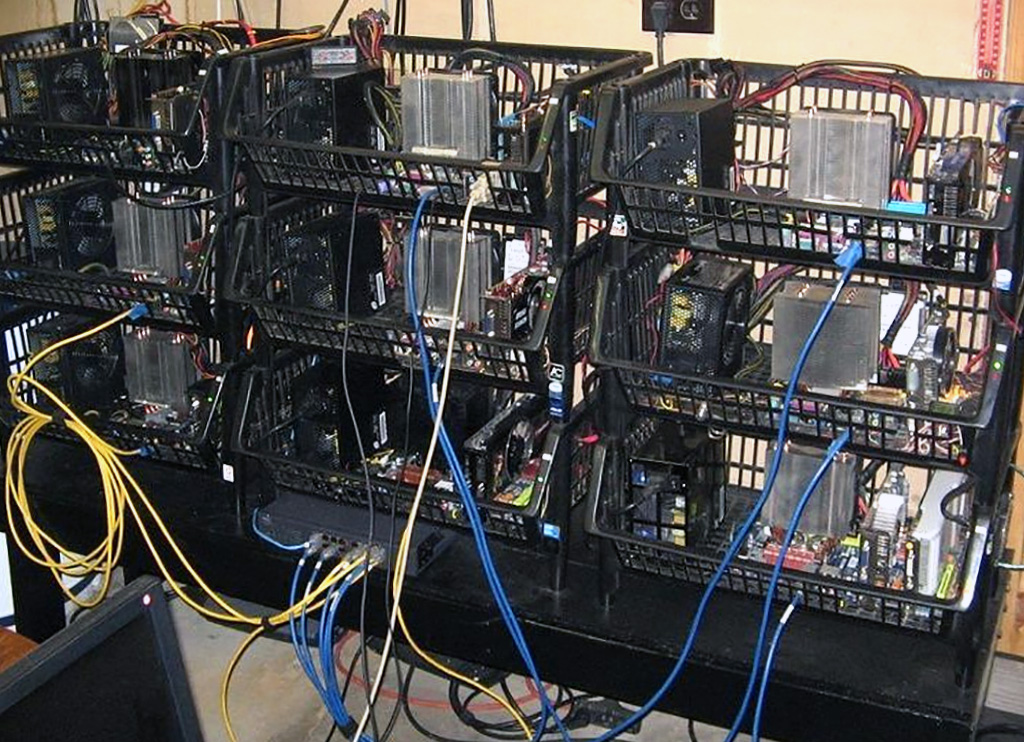
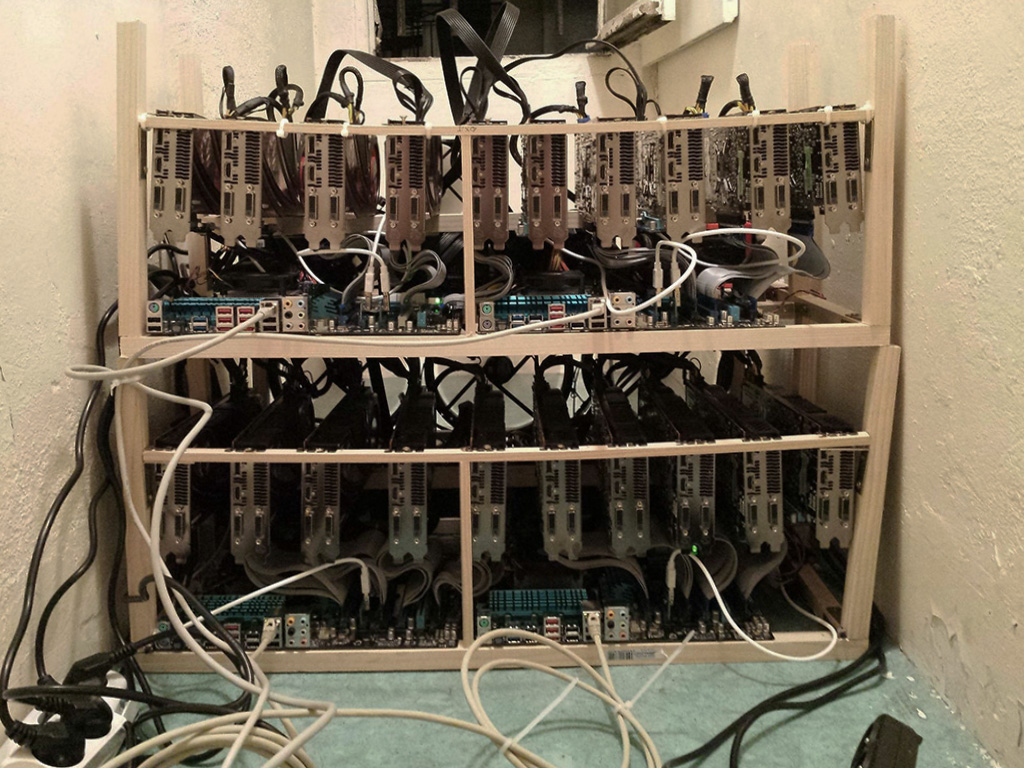
This design research project explores the creation of counter-proposals to the current expression of “Cloud Computing”, particularly in its forms intended for private individuals and end users (“Personal Cloud”). It is to offer a critical appraisal of this “iconic” infrastructure of our modernity and its user interfaces, because to date their implementation has followed a logic chiefly of technical development, governed by the commercial interests of large corporations, and continues to be seen partly as a purely functional, centralized setup. However, the Personal Cloud holds a potential that is largely untapped in terms of design, novel uses and territorial strategies. Through its cross-disciplinary approach, our project aims at producing alternative models resulting from a more contemporary approach, notably factoring in the idea of creolization (Glissant, 1990). From a practical standpoint, the project is intended to produce speculative versions of the “Personal Cloud” in the form of prototypes (whether functional or otherwise) of new interfaces, data processing, reactive environments and communicating objects. To do this, the project will be built around three dimensions forming the relevant pillars of a cross-disciplinary approach: interaction design, the architectural and territorial dimension, and the ethnographic dimension.
Continue Reading…